Every car operates differently on unstable or slippery surfaces depending on its drive type: front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), full-time 4-wheel drive (AWD), or part-time 4-wheel drive (4WD). It’s important to understand how your car’s drive system works.
Front-wheel drive (FWD): In FWD cars, the engine power is transmitted to the two front wheels. This type of drive is commonly used in models like the Chevrolet Cruze, Sonic, and Spin. FWD is popular due to its simple and compact layout, which saves fuel and increases interior space. Additionally, having the weight of the engine and transmission on the drive wheels at the front provides good traction. FWD cars tend to understeer in sharp corners and struggles in difficult terrain conditions.
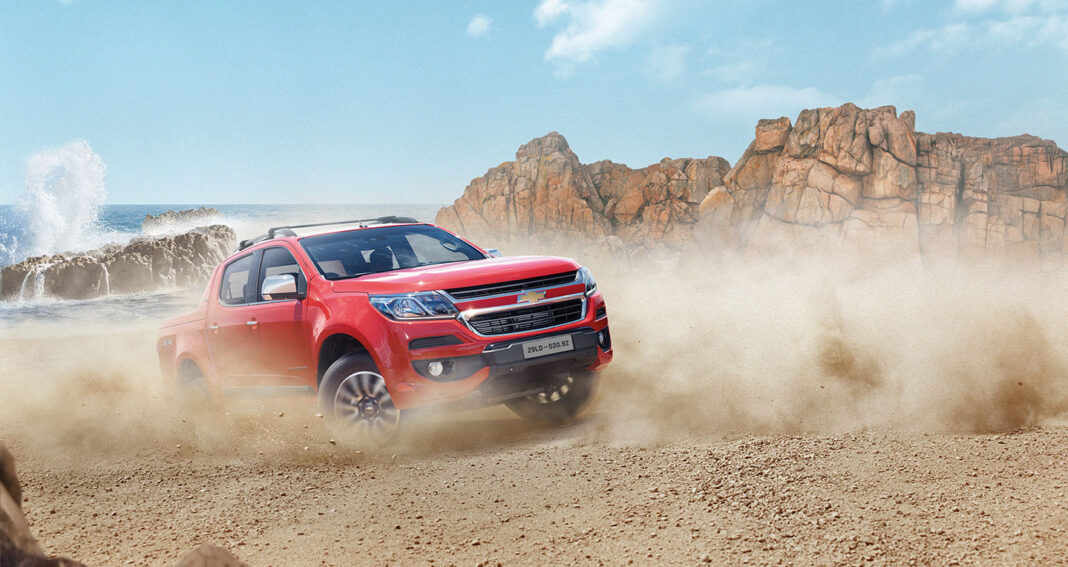
Rear-wheel drive (RWD): In RWD cars, the engine power is transmitted to the two rear wheels. RWD was dominant until the 1980s when FWD became popular. However, RWD is still more efficient in heavy cars with powerful engines. Pickup trucks, high-performance sports cars, and police cars often use RWD. The 4×2 variants of the Chevrolet Colorado and Trailblazer also have RWD, while the 4×4 variants partially fall into this category. RWD cars tend to oversteer, meaning they turn more than desired by the driver. This characteristic can cause wheels to slide or spin in difficult terrain, making it more dangerous.
All-wheel drive (AWD): AWD should not be confused with part-time 4-wheel drive (4WD). AWD operates similarly to FWD or RWD, with most AWD cars being primarily front-wheel drive. AWD calculates and transfers power to the front and rear axles to prevent wheel slip. It then reverts to front-wheel drive if there is no wheel slip. AWD provides excellent on-road performance and good traction in light off-road conditions like grass, mud, sand, or gravel. AWD tends to understeer when entering sharp corners.
Part-time 4-wheel drive (4WD or 4×4): Part-time 4WD is commonly found in pickup trucks, rear-wheel drive vehicles, and larger SUVs. It often comes with a 2-speed auxiliary transmission for maximum traction. Part-time 4WD operates in rear-wheel drive mode until all four wheels’ traction is required. The 4×4 variants of the Chevrolet Colorado and Trailblazer have a part-time 4WD system. Full-time 4WD vehicles always have power delivered to all four wheels. The torque distribution ratio can switch to 50/50 in off-road or slippery road conditions. On full-time 4WD vehicles, the driver can manually adjust the torque distribution level.
To improve traction in low-grip situations, car manufacturers have developed electronic systems like Electronic Traction Control and Electronic Stability Programs. SUVs and pickup trucks, such as the Chevrolet Colorado and Trailblazer, offer features like Hill Descent Control and Hill Start Assist to enhance performance on slippery and off-road conditions.
By understanding your car’s drive system, you can have a safer and more effective driving experience.






































![[CAR REVIEW] Range Rover Evoque 2022: Radiating opulence and distinction](https://vnauto.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Xehay-RREvoque-23082022-17-100x70.jpg)
