Electric vehicles (EVs) and vehicles powered by hydrogen or fuel cells (FCEVs) are vying to become the “future of transportation,” much like how gasoline and diesel vehicles competed in the early days.
As the world moves towards sustainable transportation, hydrogen-powered and electric vehicles are emerging as viable alternatives to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Governments worldwide are supporting consumers in transitioning from ICE vehicles to clean fuel vehicles by implementing policies that encourage the purchase and use of green vehicles.
While electric vehicles have a significant advantage and hold the promise of becoming the future of transportation, mainly thanks to Tesla, we are still in the early stages of the electric vehicle era, and nothing is set in stone. Hydrogen-powered vehicles are seen as potential competitors to electric vehicles due to their unique benefits and potential superiority.
Like electric vehicles, hydrogen-powered vehicles (also known as fuel cell electric vehicles or FCEVs) do not emit harmful pollutants on the road, and both rely on electric motors to power the vehicles. However, unlike electric vehicles that require a relatively long charging time, hydrogen vehicles can be refueled quickly, similar to gasoline or diesel vehicles. The following highlights the similarities and differences between EVs and FCEVs.
What are electric vehicles and how do they work?
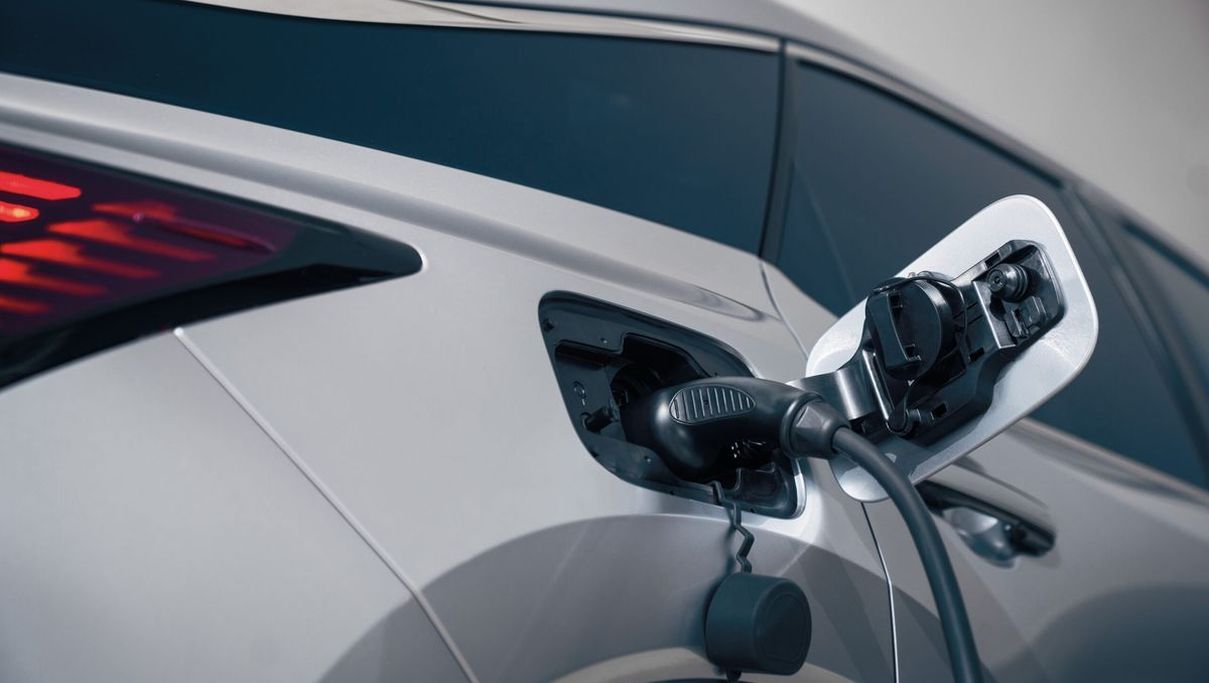
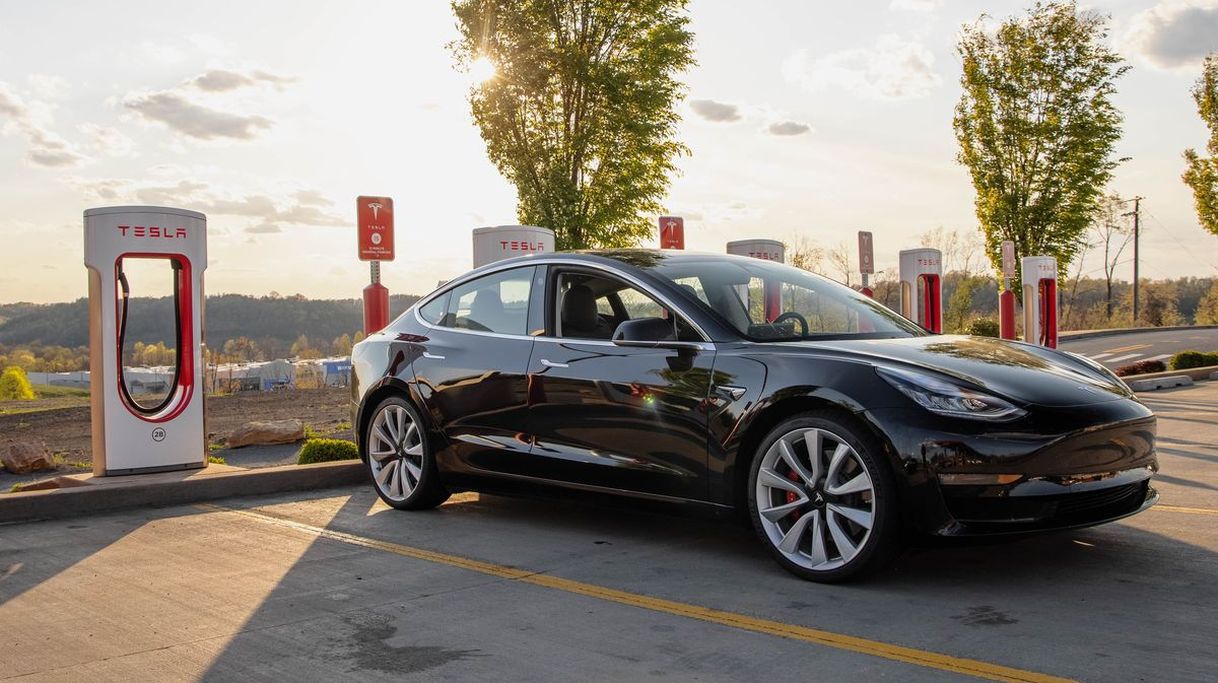
Essentially, electric vehicles are relatively simple machines. They store their main power source as chemical energy in a battery, which is then converted back into electrical energy by the vehicle’s electrical system.
Modern electric cars typically use a lithium-ion battery pack located underneath the vehicle’s floor, which powers the wheels. Electric cars emit clean and pollution-free energy into the atmosphere, making them better for the environment compared to traditional gasoline and diesel cars.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of electric vehicles?
According to Car and Driver, some advantages and disadvantages of electric vehicles include:
Advantages: Efficiency; Clean engines and lower maintenance.
Disadvantages: Limited battery life; Charging time and weak charging infrastructure.
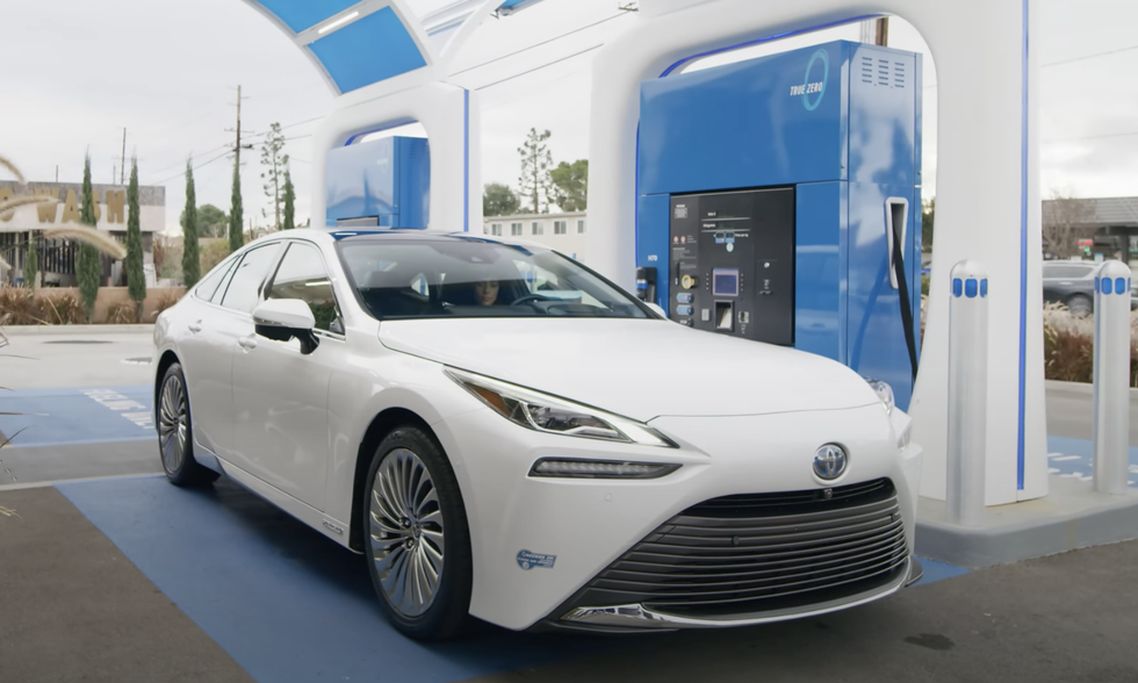
What are hydrogen-powered vehicles and how do they work?
Hydrogen-powered vehicles are much more complex than electric vehicles. Hydrogen is pumped into the vehicle’s storage tank and stored under high pressure. Since hydrogen has a lower energy density than gasoline or diesel, it needs to be compressed to provide enough gas for the vehicle.
Next, hydrogen is released into a “fuel cell.” Here, positive and negative terminals separate the hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons. The protons become water (the only emission released by a hydrogen-powered car), while the electrons supply energy through a small stored battery before being sent to the motor that drives the wheels.
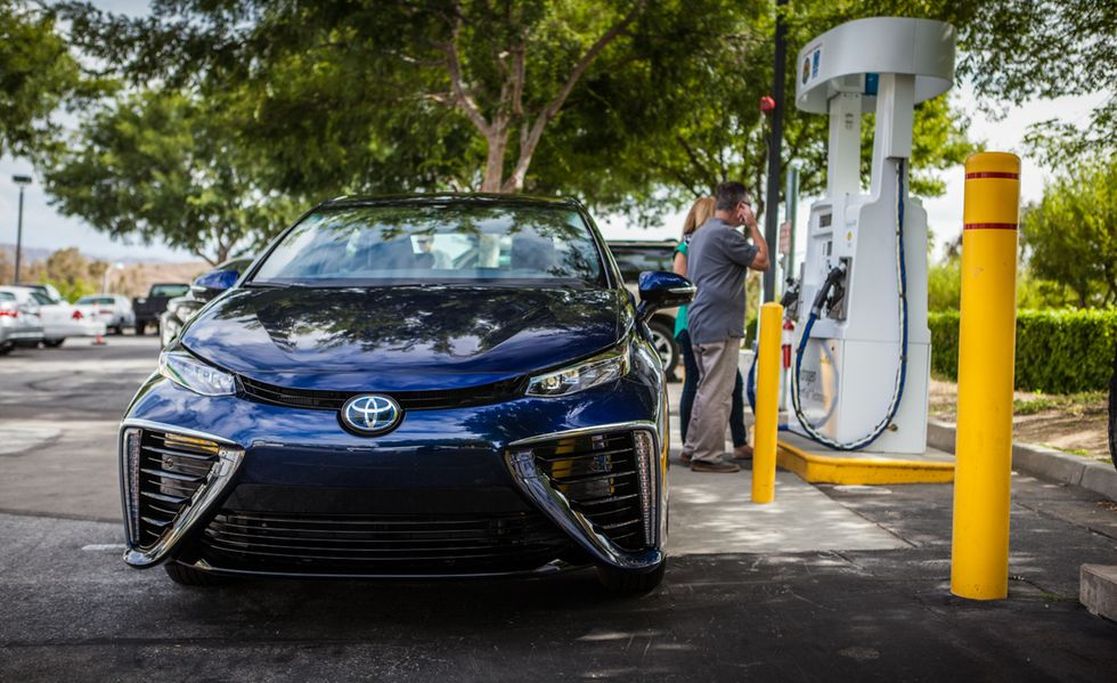
Hydrogen vehicles can be refueled within minutes at dedicated hydrogen refueling stations and can achieve long distances (643 km or more), comparable to gasoline-powered vehicles.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen-powered vehicles?
Advantages of FCEVs: Reliable technology; Fast refueling.
Disadvantages of FCEVs: Complex and expensive production; Prone to fires if not properly stored; Limited infrastructure.
How are EVs and FCEVs similar and different?
When comparing and contrasting these two types of clean fuel vehicles, several key points should be considered. At present, electric vehicles have the upper hand due to wider industry adoption, government support, and a significantly larger infrastructure. While electric vehicles still have a long way to go, hydrogen-powered vehicles face an even longer journey to gain wider acceptance among consumers.
One area where fuel cell electric vehicles have an advantage over electric vehicles is refueling. While many electric vehicles can charge faster than ever, they still cannot refuel as quickly as gasoline-powered vehicles, just as it takes time to refill a liquid hydrogen tank for FCEVs.
Both types of vehicles generate electricity and emit no harmful exhaust gases, resulting in a significantly lower environmental impact.
TT (Tuoitrethudo)
Reference: Carwow, Motorbiscuit





































![[Quick Review] Hyundai IONIQ 5 – A Vehicle from the Future](https://vnauto.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/xehay-hyundaiioniq5-18052022-2-150x150.jpg)













