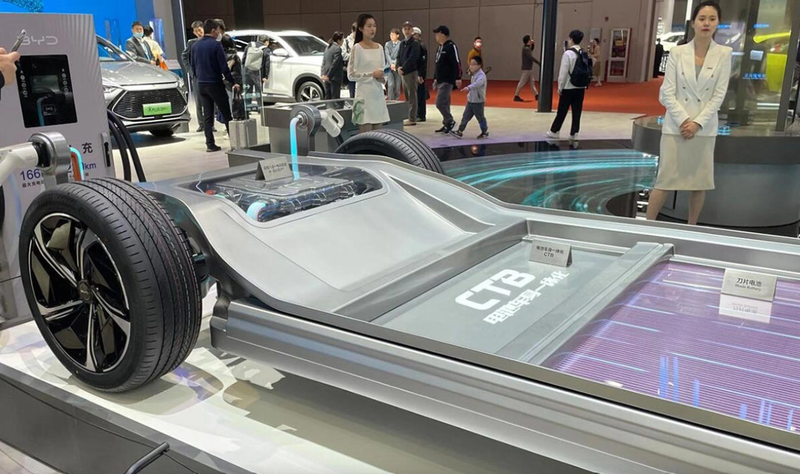
With LFP battery production costs now half of what they were last year, electric vehicle prices are predicted to drop significantly and may even reach parity with gasoline-powered cars.
According to Bloomberg, a reputable US-based economic magazine, the cost of producing lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries in 2024 is estimated to be 51% lower than in 2023. In reality, this has already happened in China, where the average battery price has dropped from $95/kWh in 2023 to $53/kWh this year.
Bloomberg attributes the steep decline in LFP battery prices in China to the significant reduction in the cost of cathode materials – the most expensive component in electric vehicle batteries. At the beginning of 2024, LFP battery cathodes were 50% cheaper than the year before. The price of this material has continued to fall in the first half of the year. As of July 2024, the price of LFP battery cathodes is just 30% of what it used to be.
Additionally, lower-than-expected demand for electric vehicles has also played a significant role in the drop in battery prices. Even Tesla, the world’s leading electric car manufacturer, operated at only 43% of its factory capacity in Shanghai in 2023, down from 51% in 2022.
In China, the price of electric vehicles using LFP batteries is now on par with gasoline-powered cars in the same segment. In other regions, this type of battery is less common than nickel-manganese-cobalt batteries, so electric vehicle prices remain slightly higher on average than their gasoline counterparts.
Nevertheless, the price decline will continue to spread to markets outside of China as Chinese automakers like SAIC, Xpeng, and BYD aggressively expand their global market share. This will force electric vehicle manufacturers from the US, Europe, South Korea, and Japan to adjust their pricing strategies to remain competitive and protect their market share.
Thai Son (Tuoitrethudo)