|
|
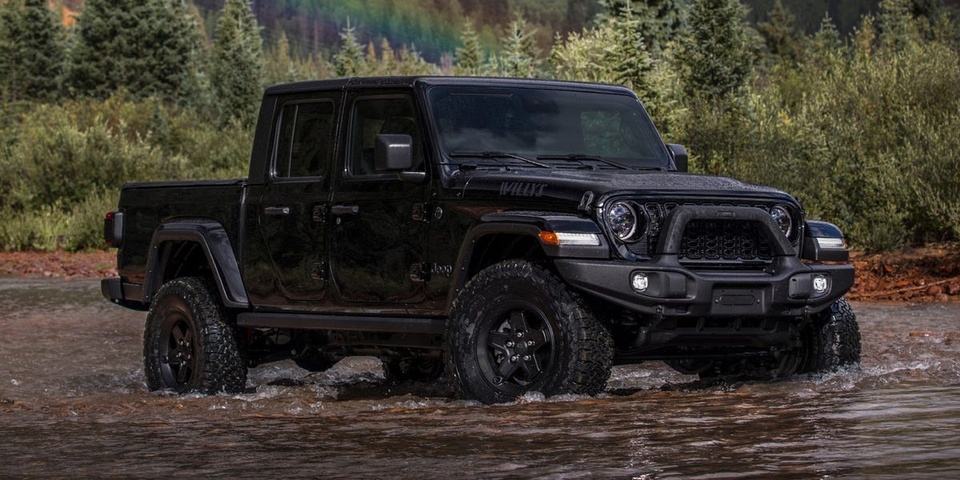
Image source: Car and Driver |
Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) is a technology that delivers power from the engine to all four wheels of a vehicle. This system enhances traction, improving the vehicle’s ability to navigate challenging terrain.
4WD is commonly found in off-road vehicles and pickup trucks such as the Toyota Hilux, Jeep Wrangler, Gladiator, and Ford Ranger, Raptor. These vehicles benefit from the increased traction and control that 4WD provides.
How does 4WD work?
The 4WD system in automobiles consists of four main components: a transfer case, a differential, sensors, and an ECU (Engine Control Unit). The differential plays a crucial role in adjusting wheel rotation speed and distributing torque between the axles.
Electronic sensors monitor wheel speed, steering angle, acceleration, and road conditions. This data is then sent to the ECU, which adjusts the traction delivered to each wheel. The driver’s ability to control and switch between different drive modes depends on whether the vehicle has a part-time or full-time 4WD system.
In part-time 4WD vehicles, the driver can fine-tune the system using a button or lever. On the other hand, full-time 4WD systems automatically distribute traction continuously, similar to AWD systems.
| |
|
4WD systems are commonly found in off-road vehicles designed for challenging terrain. Image: Bo Ha |
Vehicles equipped with 4WD are well-suited for harsh terrain as they can distribute traction to all four wheels. Additionally, some 4WD systems feature a differential lock mechanism, further enhancing their ability to overcome obstacles.
As such, 4WD is ideal for off-road vehicles that frequently encounter demanding terrain and weather conditions. A sturdy chassis coupled with a 4WD system is key to navigating challenging environments.
Heavier vehicles with higher fuel consumption
Due to their complex configuration and additional components, 4WD vehicles are typically 200-400 kg heavier than their 2WD counterparts. Consequently, they tend to have lower efficiency when traveling long distances. The intricate nature of 4WD systems also makes maintenance and repairs more costly.
Furthermore, 4WD vehicles consume significantly more fuel, approximately 10-15% more than 2WD vehicles. For example, the Toyota Hilux with 4WD has a fuel consumption rate of 7.5-9.5 liters per 100 km, while the 2WD version consumes only 6.5-8 liters per 100 km.
Recommended reads for your journey
Our ‘Xe’ category offers a diverse range of captivating books to accompany you on your travels. Whether you’re embarking on a road trip or enjoying a moment of respite, these books are the perfect companions for your journeys.
The Ultimate Off-Roader – Unveiling the Arctic Trucks’ Land Cruiser 250 Makeover
The Toyota Land Cruiser has been given a formidable makeover by Arctic Trucks, now standing tall with an aggressive stance. This beast of a vehicle has been elevated to new heights, quite literally, with a 40 mm increase in height and massive 37-inch tires. These enhancements allow the Land Cruiser to effortlessly traverse a variety of terrains, making it a true off-road champion.