In a bold move to control e-waste and safeguard strategic resources, the Chinese government has introduced stringent new regulations on electric vehicle battery recycling.
Effective April 1, 2026, discarded batteries must remain with the vehicle and cannot be removed independently. This decisive step aims to standardize the entire supply chain and waste management process in the world’s largest electric vehicle producer.
Ending the Era of Risky, Unregulated Battery Removal
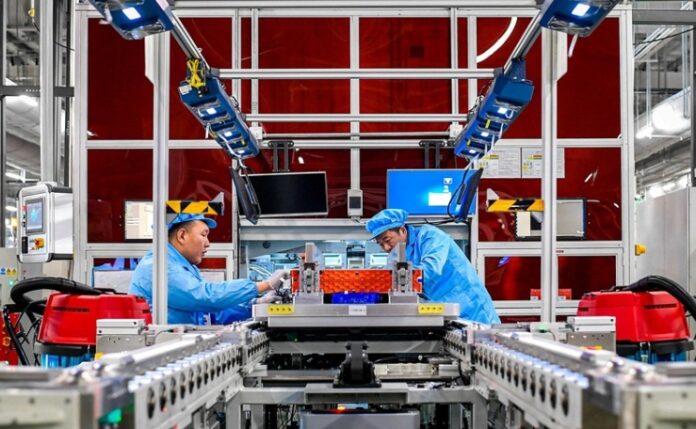
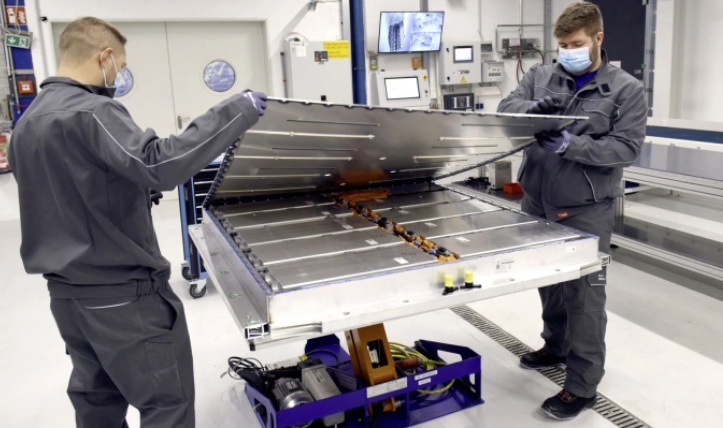
Historically, battery recycling in China has faced significant safety and environmental challenges. Manual dismantling, often performed incorrectly, posed fire hazards and contaminated water and soil due to leaking toxic chemicals. With modern electric vehicle batteries becoming larger and more integrated into vehicle chassis, their removal requires advanced techniques beyond the capabilities of small, unregulated facilities. The new regulation ensures batteries remain intact with the vehicle, guaranteeing they reach authorized recycling centers instead of the black market.
National Tracking System for Full Lifecycle Management
To address systemic inefficiencies, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has launched a national platform to track each battery’s entire lifecycle. Every battery produced will carry a unique identifier compliant with the GB/T 34014 standard. This code enables authorities to trace batteries from production and sales to repair, disposal, and recycling. Manufacturers and importers must submit detailed technical data and dismantling procedures within six months of product certification, creating a transparent and comprehensive data ecosystem.
Expanding Recycling Responsibilities and Unlocking a Billion-Dollar Market
A key innovation in these regulations is the expanded responsibility for both battery manufacturers and new energy vehicle retailers. These entities must establish collection stations in high-consumption areas and provide clear contact information for customers. Only licensed companies can participate in the comprehensive processing of discarded batteries, preventing unauthorized handling. With projections of up to 1 million tons of battery waste by 2030, the recycling market is poised to reach $78 billion by 2025, led by industry giants like Brunp Recycling (a CATL subsidiary).
Sustainable Secondary Resource Management Strategy
This tightened regulation is not just an environmental measure but a strategic resource management initiative. Current technology allows Chinese companies to recover 99.6% of valuable metals like nickel, cobalt, and manganese, and 96.5% of lithium from used batteries. By mandating centralized, professional recycling, China transforms waste into a critical secondary resource, reducing reliance on natural mineral extraction. This shift from rapid development to sustainable management solidifies China’s leadership in the global electric vehicle revolution.
TH (Tuoitrethudo)
Electric Vehicle Battery Recycling: Uncovering the Gold Mine in the Green Revolution
The transportation industry is undergoing a revolutionary shift with the rise of electric vehicles, and the recycling of EV batteries is emerging as a promising sector. With an impressive growth rate and an ever-increasing economic value, the EV battery recycling industry is poised to become a significant player in the sustainable future of mobility.
Electric Dreams: Revolutionizing Recycling with a Visionary Center for EV Battery Renewal
“Ho Chi Minh City aims to take a giant leap forward in its transition to electric mobility and circular economy ambitions with plans to develop a state-of-the-art electric vehicle battery recycling center. The facility is designed to recover up to 95% of precious metals, setting a new standard in sustainable practices and positioning the city at the forefront of eco-friendly innovation.”